To run a Python script, just type python and then the script's file name. You must be in the same directory as the script, otherwise you must give python the relative path to the script. This means that in order to run python scripts in the lt-maker directory, you should run python from within the lt-maker directory. Python Command Not Found. The.python:build job template provides an end-to-end distribution build configuration, effectively running the following command to build a project: python -m build -sdist -wheel. The outputs are uploaded as job artifacts. The following variables can be used to configure the build. This page contains links to a variety of examples that can help you understand how to implement GitLab CI/CD for your specific use case. Examples are available in several forms. As a collection of:.gitlab-ci.yml template files maintained in GitLab, for many common frameworks and programming languages. Repositories with example projects for. To run these tests automatically when you push code to your repository, add the following job to your.gitlab-ci.yml. Test:pytest: image: python:3.6 script: - pip install pytest -quiet - pytest. Pytest will automatically discover all test files in your project (all files named test.py.
- Gitlab Ci/cd Run Python Script
- Gitlab Ci Run Python Script Example
- How Make A If Statement In The CI File
- Gitlab Runner Run Python Script
How does GitLab integrate with Maven?
Create the simple Maven dependency
- Log in to your GitLab account.
- Create a new project by selecting Import project from ➔ Repo by URL.
- Click Create project.
How do I run a Python script from GitLab?
Automating python scripts to run by GitLab CI (Runner) needs to configure with “….In order to schedule a pipeline:

- Navigate to your project’s CI / CD > Schedules and click the New Schedule button.
- Fill in the form.
- Hit Save pipeline schedule for the changes to take effect.
How do I deploy a GitLab project?
Using GitLab to deploy project pages
- Step 1: Create a repository for your project pages.
- Step 2: Add content to the repository.
- Step 3: Add continuous integration through .
- Step 4: Deploy and test your new project pages.
How do you write CI CD in GitLab?
- Get started. CI/CD concepts Migrate from CircleCI Migrate from Jenkins Enable or disable CI/CD.
- Pipelines.
- Choose when jobs run Access a terminal for a running job Format scripts and job logs Git submodules.
- Variables.
- Environments and deployments.
- Runners.
- Cache and artifacts.
- .gitlab-ci.yml.
How do you continuously deploy?
Moving from continuous delivery to continuous deployment
- Emphasize a culture of continuous integration.
- Make sure you have good test coverage (and good tests too!)
- Adopt real-time monitoring.
- Review your post-deployment tests.
- Get your QA team to work upstream.
- Drop the traditional release notes.
Is continuous delivery is different from continuous deployment?
The key difference is that with Continuous Deployment, your application is run through an automated pipeline workflow. Whereas with Continuous Delivery, your application is ready to be deployed whenever your team decides it’s time to do so.
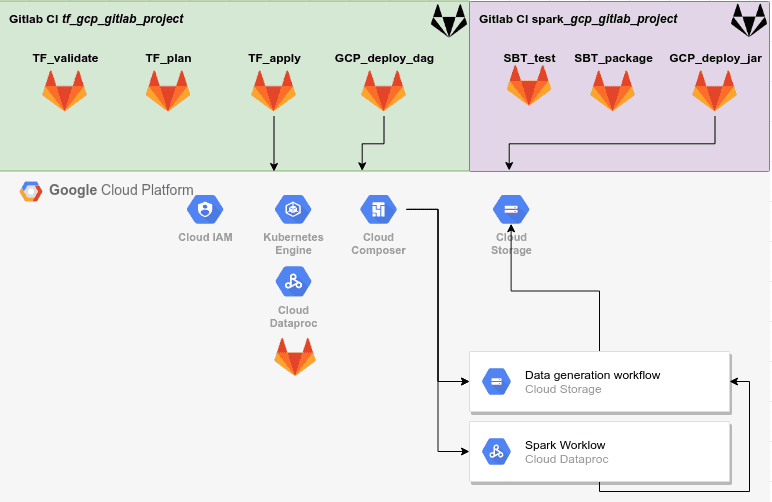
This blog specifies how to automate python scripts to run by GitLab CI. Inthe following, I will talk about each element of the configuration with“.gitlab-ci.yml”, manage environments with anaconda and “environment.yml”, andsettings on GitLab.
Requirements
Before all, I would like to specify my working environment.
- OS: Debian 8
- GitLab Community Edition 10.8.0 (GitLab Installation)
- GitLab Runner (GitLab Runner Installation)
- Python 3.6.4
Project structure
Using GitLab CI to configure your jobs
.gitlab-ci.yml is used by GitLab CI to manage your project’s jobs. It isplaced in the root of your repository and contains definitions of how yourproject should be built. On any push to your repository, GitLab will look forthe .gitlab-ci.yml file and start jobs on CI according to the contents ofthe file, for that commit.
Following is one example:
In this example, there are several parts: stages, image, stage, script,only, tags. I’ll introduce them one by one.
stages
stages is used to define stages that can be used by jobs and is definedglobally.
The specification of stages allows for having flexible multi stage pipelines.The ordering of elements in stages defines the ordering of jobs’ execution:
- Jobs of the same stage are run in parallel.
- Jobs of the next stage are run after the jobs from the previous stage completesuccessfully.
In the example, we have 2 stages ‘test’ and ‘report’. The jobs of stage ‘test’will run before running the jobs of stage ‘report’.
image
This allows to specify a custom Docker image that can be used for time of thejob. In our case, we need to use connect Teradata which officially supports onlyCentOS and RHEL Linux distributions, so we built upon Jeremy Marshall’sdocker-teradata-client container and moble’s miniconda-centoscontainer.
If the configuration interests you, more information here.
stage
Gitlab Ci/cd Run Python Script
stage is defined per-job and relies on stages which is defined globally. Itallows to group jobs into different stages, and jobs of the same stage areexecuted in parallel.
In the example, the job in ‘tests’ corresponds the stage ‘test’, the job in‘weekly_job’ corresponds the stage ‘report’.

script
script is the only required keyword that a job needs. It’s a shell scriptwhich is executed by the CI.
The scripts in ‘tests’ update pip, install packages in requirements.txt with pip,and discover unit tests that ends with ‘_test.py’.
We created a conda environment quietly from file jobs/environment.yml (I’ll talkabout this file in the next part), then switching to the new environment whichis defined by the file, and run python script jobs/weekly_job.py by python.
only
only defines the names of branches and tags for which the job will run.

There are a few rules that apply to the usage of job policy:
onlyis inclusive. If only is defined in a job specification, the ref isfiltered by only.onlyallows the use of regular expressions.onlyallows to specify a repository path to filter jobs for forks.
In addition, only allows the use of special keywords. For example, variableskeyword is used to define variables expressions, in other words you can usepredefined variables / project / group or environment-scoped variables to definean expression GitLab is going to evaluate in order to decide whether a jobshould be created or not; using refs to specify that a branch is pushed andscheduled pipelines.
In the example, the job only runs when it satisfies the following conditions:
- value of variable $weekly_job is “yes”(use
%variable%in windows batch and$env:variablein PowerShell) - following the scheduled pipelines
- script is on the master branch
tags
tags is used to select specific Runners from the list of all Runners that areallowed to run this project.
Managing environments
With conda, you can create, export, list, remove and update environments thathave different versions of Python and/or packages installed in them. Switchingor moving between environments is called activating the environment. You canalso share an environment file.
Creating an environment from an environment.yml file
You can create an environment file manually to share with others.
An environment.yml file should specify environment’s name with name, anddependable packages with dependencies.
Gitlab Ci Run Python Script Example
GitLab settings
Configuring GitLab CI
A Runner can be specific to a certain project or serve any project in GitLab CI.A Runner that serves all projects is called a shared Runner. You can find moreinformation about configuration here.
Before running, don’t forget to go to Settings > CI/CD > Runners settingsto active your runner.
Pipeline Schedules
How Make A If Statement In The CI File
Pipeline schedules can be used to run a pipeline at specific intervals, forexample every Monday at 7:00 for a certain branch.
In order to schedule a pipeline:
- Navigate to your project’s CI / CD > Schedules and click the New Schedule button.
- Fill in the form
- Hit Save pipeline schedule for the changes to take effect.
Moreover, You can pass any number of arbitrary variables and they will beavailable in GitLab CI so that they can be used in your .GitLab-ci.yml file.